When it comes to controlling companies with a high level of fixed assets, I strongly recommend learning how to budget and control your CAPEX. Mastering your CAPEX is important for controlling how you allocate your capital.
In that light, let’s learn everything about CAPEX, the CAPEX Definition, and how to budget and control your CAPEX.
CAPEX Meaning
CAPEX (short for capital expenditures) is the money spent by a business to purchase, maintain, or improve fixed assets.
It can include real estate, buildings, factories, equipment, and technology.
Therefore, organizations use this kind of financial investment to broaden the scope of their activities. And to add some potential economic gain.
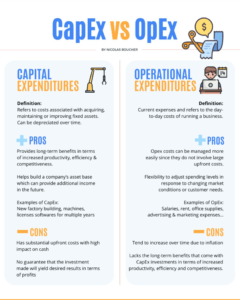
CAPEX VS. OPEX
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of both CAPEX and OPEX.
Pros of CAPEX
- Capex investments provide long-term benefits in terms of increased productivity, efficiency and competitiveness.
- They also help build a company’s asset base, which can provide additional income in the future.
Cons of CAPEX
- Capex investments involve substantial upfront costs, which can strain an organization’s finances if not managed properly. In addition, there is no guarantee that the investment will yield the desired results in terms of increased profits or competitive advantage.
Pros of OPEX
- You can manage OPEX costs more easily than CAPEX investments. The reason for this is that they do not involve large upfront costs, and there is no need for long-term commitments.
- They also provide the flexibility to adjust spending levels in response to changing market conditions or customer needs.
Cons of OPEX
- Opex costs tend to increase over time due to inflation and other factors, which can strain an organization’s finances if not managed properly. In addition, OPEX expenditures may lack the long-term benefits that come with CAPEX investments. This is in terms of increased productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness.
CAPEX Controlling:
Here are my 6 steps process for Capex budgeting and control
- Definition of your Capex
- Examples of CAPEX
- Funding of CAPEX
- Prioritization
- Phasing
- Cash
- Reporting
- How do you control Capex?
Let’s discuss each step thoroughly.
1) Definition of Your Capex and Why Is It Important to Learn How to Budget and Control Your Capex
First, you should know how to define your CapEx.
CAPEX is short for capital expenditures. In the context of finance and accounting, CAPEX refers to the amount of money a company spends to acquire, maintain, or improve its physical assets, such as property, buildings, and equipment. This type of expenditure is considered a capital expenditure because it is expected to generate future economic benefits for the company over a period of time, usually more than one year.
CAPEX is important to a company’s financial health because it can lead to increased productivity and efficiency, which can ultimately result in increased profits. However, it is also important for a company to carefully manage its CAPEX to ensure that it is being used efficiently and effectively.
2) Examples of CAPEX Include:
- Purchasing a new production facility or a piece of machinery
- Constructing a new building or making renovations to an existing one
- Upgrading or replacing equipment or software
3) Funding of CAPEX
CAPEX is typically funded through a company’s internal resources, such as retained earnings, or through external sources, such as loans or equity financing. In contrast to operating expenses, which are expenses incurred in the day-to-day operations of a business, CAPEX is a non-recurring expense that is not required to sustain the current level of operations.
3) Categorization Is Important to Know How to Budget and Control Your CAPEX
Evaluate If It Is A CAPEX or OPEX
The first step when you want to control your CAPEX is to know if your expenditure can be capitalized (CAPEX) or should be fully expenses (OPEX).
Assign The Right Fixed Asset Category
To assign the right fixed asset category and corresponding depreciation method for CAPEX, it is important to consider the following factors:
Nature of the asset: The type of asset being acquired will determine the appropriate category for it. For example, the land is a fixed asset that does not depreciate, whereas buildings and equipment will depreciate over time.
Use of the asset: The intended use of the asset will also determine the appropriate category. For example, an asset used in the production of goods for sale would likely be classified as a production asset, while an asset used for administrative purposes would be classified as an administrative asset.
How to Budget and Control your CAPEX with The Depreciation Method
The appropriate depreciation method should be chosen based on the expected useful life of the asset and the pattern of the asset’s usage. Some common depreciation methods include straight-line, declining balance, and sum-of-the-years’-digits.
It is important to properly classify and depreciate fixed assets. Since this information is used to accurately reflect the company’s financial position and performance in its financial statements. This is also required for tax purposes, as different depreciation methods may result in different tax deductions.
Types of CAPEX Are Key to Know How to Budget and Control your CAPEX
CAPEX can be classified into different types based on the purpose for which it is being incurred. Some common types of CAPEX include:
Recurring: Recurring CAPEX refers to regular expenditures that a company makes to maintain or improve its existing assets. These expenses are typically necessary to sustain the current level of operations and may include repairs, maintenance, and upgrades to existing equipment and facilities.
One-off: One-off CAPEX refers to a single, large expenditure that a company makes to acquire or improve a specific asset. This type of expenditure is not expected to be repeated on a regular basis.
Growth: Growth CAPEX refers to expenditures that are made to support the expansion or growth of a company’s operations. This may include investments in new facilities, equipment, or technology to support the production of additional goods or services.
Replacement: Replacement CAPEX refers to expenditures made to replace an existing asset with a newer, more efficient one. This type of expenditure is typically made when the existing asset has reached the end of its useful life or when it is no longer cost-effective to continue maintaining it.
To identify the type of CAPEX, it is important to examine the purpose and expected benefits of the expenditure. You can find this in the company’s financial statements and other supporting documentation, such as investment proposals or business plans. It is also important to consider the timing of the expenditure, as well as any patterns or trends in the company’s CAPEX over time.
4) Prioritization
Nest, classify the future investments based on their importance for your organization and their ROI. Also, make sure it’s aligned with the strategy!
Here are some examples of classification:
- Growth
- New products
- Cost savings
- Risk mitigation
- Compliance and security needs
5) Phasing
Furthermore, you need to plan the phasing of your investments.
CAPEX phasing refers to the process of breaking down your capital expenditure budget into smaller, more manageable amounts that can be incurred over a period of time. This approach can be useful for a variety of reasons, such as:
Managing cash flow: Phasing CAPEX over a longer period of time can help a company spread out the cost of the expenditure. That makes it easier to manage its cash flow.
Reducing risk: By phasing CAPEX, a company can spread out the risk associated with the expenditure over a longer period of time. This can be especially useful for large, risky investments, as it allows the company to assess the performance of the investment before committing additional resources.
Improving decision-making: Phasing CAPEX can also help a company make more informed decisions about its investments. By breaking the expenditure down into smaller increments, a company can gather more information about the investment and make any necessary adjustments before committing additional resources.
Here is what you need to do in your budget and forecast to make sure you monitor the phasing of your capital expenditures:
For each of the significant lines of investment, you need to assign the following:
- The date (or the month or quarter) you want to order the investment
- The date your investment will be delivered and operational
6) Cash
You should evaluate the cash impact of your investment:
For a small investment, define in which quarter the cash will come.
For bigger capital expenditures, you need to:
- prepare a cash curve based on the payment milestones
- identify the necessary resources and financing options in advance
If the cash spent is significant, you can also perform a cost-benefit analysis.
A cost-benefit can help a company evaluate the expected benefits and costs of a CAPEX expenditure. This method can help a company determine the optimal way to allocate its resources. Additionally, it also helps reduce the impact on its cash flow as it will look at optimizing cash utilization.
7) Reporting
Another key point when controlling CAPEX is reporting.
Make sure to record and report periodically against the budget the following actuals:
- Investments approved: compare the number of investments approved with the investments planned
- Investments ordered: compare which ones are already ordered from your suppliers. This is important because an investment order means the company has a commitment. As CAPEX represents a significant amount of cash outflows, it can have a significant impact on the cash.
- Acquired Investments: compare the investments which are already delivered and operational compared to your budget. Often the timing of the acquisition is optimist compared to the reality. Analyzing it can explain the difference of timing you have and the impact on your operations and financial figures, as well as the depreciation (as it delays the start of the depreciation period)
- Cash movements: compare the cash outflow compared to the planned cash movements. It helps understand the impact of your CAPEX on your cash flows.
For that reason, prepare a clear report of what is done vs what was planned and show the phasing of the Capex in progress: (validated/ordered/partly installed/fully operational/fully paid).
8) How to Budget and Control Your CAPEX?
Lastly, learning how to control everything is of the essence. Therefore, consider doing this:
- Review the priorities with management and the different departments involved. Your goal is to make sure the budget is allocated in the best interest of the organization.
- Benchmark yourself against the industry or other units (% of Capex vs sales, % of depreciation costs in hourly rate…)
As I have shown, this is a topic that concerns many professionals. Unfortunately, there is little information available on the best practice on how to budget and control CAPEX.
As finance should facilitate the Capex process and support the operations, Finance should teach the operational teams about CAPEX.
In the end, both Finance and operational departments should have the common goal of having the organization make the right investment in a timely manner.
The Bottom Line – How to Budget and Control Your CAPEX
With everything said above, it’s clear that learning how to budget and control your CAPEX is highly beneficial.
If there’s anything I could help you out with, don’t hesitate to contact me so we can engage together in one of my online courses or subscribe to my newsletter.
Key Takeaways
- CAPEX involves spending on fixed assets like real estate and equipment.
- CAPEX investments offer long-term benefits and asset-based growth.
- CAPEX differs from OPEX, which involves operational expenses.
- CAPEX is categorized, controlled, and monitored through prioritization, phasing, cash evaluation, and reporting.
- Successful CAPEX management requires collaboration between Finance and operational departments.
FAQ
1. What is CAPEX and why is it important in finance?
- CAPEX (Capital Expenditures) refers to money spent by a business to purchase, maintain, or improve fixed assets like real estate, equipment, and technology. It’s crucial because it allocates capital for long-term benefits and economic gains.
2. What are the advantages of CAPEX investments?
- CAPEX investments offer long-term benefits such as increased productivity, efficiency, competitiveness, and asset-based growth.
3. What are the differences between CAPEX and OPEX?
- CAPEX involves capital expenditures for fixed assets, providing long-term benefits, but with substantial upfront costs. OPEX involves operational expenditures for day-to-day activities, with more flexibility but increasing costs over time.
4. How can I categorize and control CAPEX?
- Categorization: Distinguish between CAPEX and OPEX expenditures based on capitalization rules. Prioritization: Evaluate future investments and classify them based on importance and ROI. Phasing: Break down CAPEX budgets into manageable amounts to manage cash flow and reduce risk. Cash: Evaluate cash impact, prepare a cash curve, and consider financing options. Reporting: Record and report actuals against the budget, track approved, ordered, and acquired investments.
5. What’s the bottom line of budgeting and controlling CAPEX?
- Mastering CAPEX budgeting and control is crucial for optimizing capital allocation and ensuring timely and effective investments for long-term benefits. Collaboration between Finance and operational departments is essential for successful CAPEX management.