Do you know how you can reduce inventory working for a manufacturing company?
Inventory management is crucial for manufacturing companies looking to optimize their cash flows and improve their bottom line. Keeping excessive inventory can tie up cash, increase storage costs, and lead to the obsolescence of products.
As a finance professional, it’s essential to implement effective inventory management strategies to reduce inventories and improve profitability. Here, I will discuss five finance-led propositions to consider when working for a manufacturing company to help reduce inventories and the top 10 inventory KPIs.
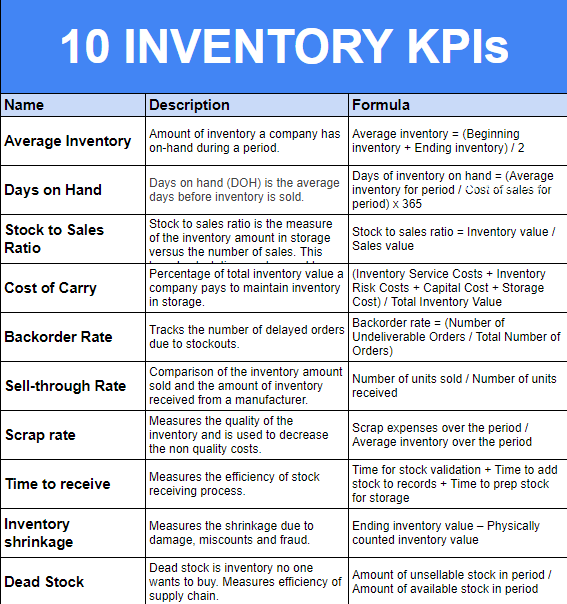
Top 10 Inventory KPIs
Here are the top 10 Inventory KPIs.
#1: Average Inventory
Description: Amount of inventory a company has on hand during a period.
Formula: Average inventory = (Beginning inventory + Ending inventory) / 2
#2: Days on Hand
Description: Days on hand (DOH) is the average days before inventory is sold.
Formula: Days of inventory on hand = (Average inventory for period / Cost of sales for a period) x 365
#3: Stock-to-Sales Ratio
Description: Stock-to-sales ratio is the measure of the inventory amount in storage versus the number of sales. This broad calculation can be used to adjust the stock to maintain high margins.
Formula: Stock to sales ratio = Inventory value / Sales value
#4: Cost of Carry
Description: Percentage of total inventory value a company pays to maintain inventory in storage.
Formula: (Inventory Service Costs + Inventory Risk Costs + Capital Cost + Storage Cost) / Total Inventory Value
#5: Backorder Rate
Description: Tracks the number of delayed orders due to stockouts.
Formula: Backorder rate = (Number of Undeliverable Orders / Total Number of Orders)
#6: Sell-through Rate
Description: Comparison of the inventory amount sold and the amount of inventory received from a manufacturer.
Formula: Number of units sold / number of units received
#7: Scrap Rate
Description: Measures the quality of the inventory and is used to decrease the non-quality costs.
Formula: Scrap expenses over the period / Average inventory over the period
#8: Time to receive
Description: Measures the efficiency of the stock-receiving process.
Formula: Time for stock validation + Time to add stock to records + Time to prep stock for storage
#9: Inventory Shrinkage
Description: Measures the shrinkage due to damage, miscounts, and fraud.
Formula: Ending inventory value – Physically counted inventory value
#10: Dead Stock
Description: Dead stock is inventory no one wants to buy. Measures efficiency of the supply chain.
Formula: Amount of unsellable stock in period / Amount of available stock in the period
Top Five Finance-Led Propositions to Reduce Inventory
Here are the top five propositions to reduce inventory.
Analyze Inventory Turnover Ratios
The first step towards reducing inventories is to analyze inventory turnover ratios. This ratio helps identify slow-moving or obsolete inventory, enabling you to make informed decisions regarding inventory management.
How to implement it?
First, to implement this strategy, you need to calculate inventory turnover ratios for different inventory categories. Then, identify slow-moving/obsolete inventory, and take measures to reduce inventory levels, such as offering discounts or promotions or liquidating inventory.
Implement Vendor-Managed Inventory
Another strategy to reduce inventories is to implement vendor-managed inventory (VMI). VMI involves the supplier managing inventory levels, reducing the need for your company to hold excess inventory.
How to implement it?
To implement this strategy, you need to identify key suppliers, establish VMI agreements with them, and work with suppliers to develop accurate demand forecasts and inventory management plans. Finally, to continuously monitor inventory levels and supplier performance.
Use Inventory Financing
Inventory financing is another effective strategy to reduce inventories. It allows you to use inventory as collateral to obtain financing, lowering the need for excess inventory and providing working capital to fund operations.
How to implement it?
To implement this strategy, you need to evaluate inventory financing options, choose a suitable financing provider, use inventory as collateral to obtain financing, and continuously monitor inventory levels to ensure sufficient collateral and timely repayment of the loan.
Implement ABC Analysis
ABC analysis involves categorizing inventory items based on their relative importance and value. That allows you to allocate resources and manage inventory levels more efficiently.
How to implement it?
To implement this strategy, you need to categorize inventory items into A, B, and C categories based on their relative importance and value. Also, set inventory targets for each category, and implement measures to reduce inventory levels for lower-value items, such as reducing safety stock levels or using just-in-time inventory management.
Implement Consignment Inventory
Consignment inventory involves storing inventory at a customer’s location until it is sold, reducing the need for the seller to hold excess inventory and improving cash flow.
How to implement it?
To implement this strategy, you need to identify suitable customers for consignment inventory arrangements and establish a consignment inventory agreement with customers outlining the terms and conditions of the arrangement. Also, continuously monitor inventory levels and customer demand to ensure timely replenishment and efficient inventory management.
The Bottom Line – Reducing Inventory is Essential for A Manufacturing Company
Reducing inventories is crucial for manufacturing companies looking to optimize their cash flows and improve their profitability. Therefore, as a finance professional, implementing effective inventory management strategies is essential to achieve these goals.
Additionally, by analyzing inventory turnover ratios, implementing VMI, using inventory financing, implementing ABC analysis, and consignment inventory, companies can reduce inventories and improve their bottom line.
Therefore, by implementing these strategies, finance professionals can help their manufacturing companies become more competitive, agile, and profitable in today’s challenging market.
Finally, if you want to become a finance professional and leverage your career, you can take my course and the ChatGPT finance guide.