In finance, there are countless theories, tools, and techniques. It can be overwhelming at times, especially when you’re trying to zero in on what’s truly essential.
When I started my career, I felt that same sense of information overload, feeling like I had to master everything to be competent.
But over time, I learned that some core concepts stand out – the kind of insights that make a real difference in decision-making and can transform a financial team’s impact on their company.
Today, I want to share with you the top four most important finance concepts. If you only focus on four, these are the ones that will give you the biggest bang for your buck.
The 4 Core Finance Concepts

Here are the 4 finance concepts, along with how to apply them, why they are important, use cases, and my pro tip.
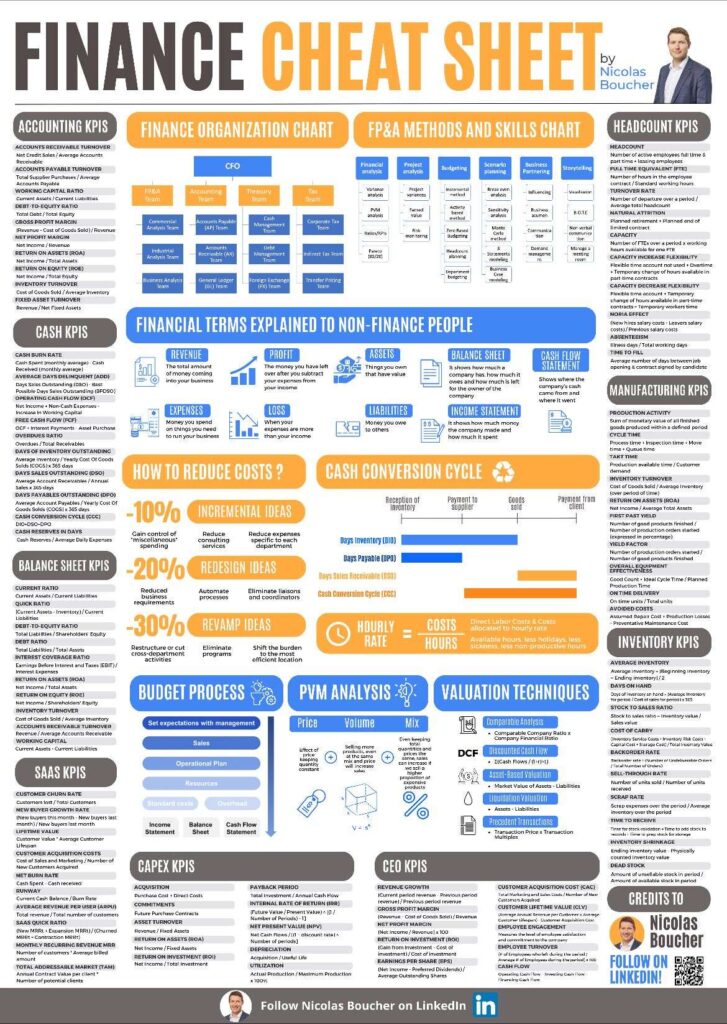
#1: PVM Analysis (Price – Volume – Mix)
Exclusively, I’ve unlocked one of my PVM Analysis Video Course lessons for you.
Components of PVM Analysis
Price
This aspect examines the impact of changes in price on sales revenue while keeping quantity constant. Understanding price effects helps determine if pricing strategies are driving profitability.
Volume
Volume refers to the number of units sold. Selling more products, even at the same price and mix, can lead to higher sales. Volume effects highlight the impact of market demand and sales efforts.
Mix
The product mix effect refers to changes in the composition of products sold. Even if the total quantity and prices remain unchanged, a shift toward selling more high-margin products can increase revenue. This component reveals how different products contribute to profitability.
Why Is It Important
PVM analysis is a powerful tool that can help a company deeply understand the drivers behind revenue changes.
It breaks down sales variances into price, volume, and product mix effects, giving finance professionals clarity on how each factor contributes to overall performance.
By understanding these components, you can take actionable steps to enhance profitability, make strategic pricing decisions, and optimize the sales mix.
Use Cases
PVM analysis is particularly useful during sales reviews.
It allows you to assess how price changes, sales volumes, and shifts in product mix have affected revenue.
For instance, if sales are down, is it because of decreased volume, a drop in price, or selling a higher proportion of less expensive products?
These insights can guide strategic decisions to improve revenue.
Pro Tip
Use PVM analysis regularly – don’t wait until things go wrong.
You can proactively adjust strategies to maximize sales performance and profitability by continuously monitoring price, volume, and mix impacts.
#2: Valuation Techniques
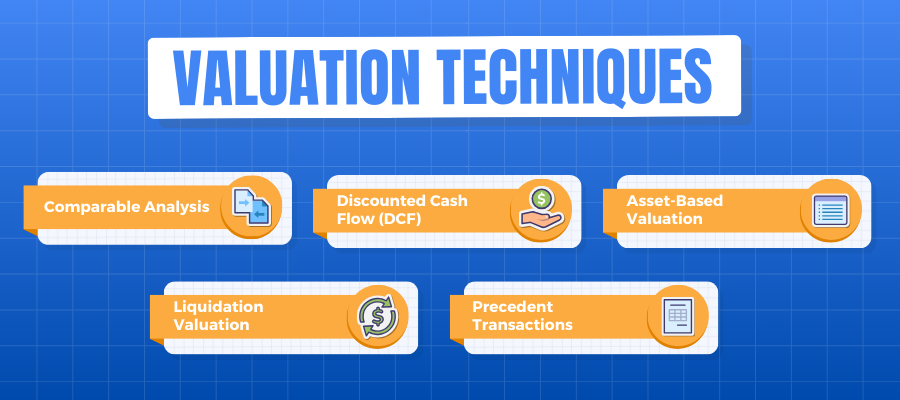
Different Valuation Methods and When to Apply Them
Comparable Analysis
Valuation ratios from similar companies (e.g., P/E ratio, EV/EBITDA) are used to determine the target company’s market-based value.
Pros:
-
- Quick and easy to implement when comparable data is available.
- Reflects current market sentiment and investor expectations.
- Useful for benchmarking against industry peers.
Cons:
-
- Prone to market inefficiencies and biases.
- Difficult to find truly comparable companies, especially for niche or unique businesses.
- Does not account for company-specific factors or future performance.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)
Involves calculating the present value of future cash flows using the formula Σ(Cash Flows / (1 + r)^t), where “r” is the discount rate. It reflects the intrinsic value of a company based on its future ability to generate cash flows.
Pros:
-
- Provides a thorough and detailed analysis of intrinsic value.
- Useful for assessing companies with predictable and stable cash flows.
- Takes into account the time value of money and risk factors.
Cons:
-
- Highly sensitive to assumptions about growth rates, discount rates, and future cash flows.
- Complex and requires substantial data and analysis.
- Difficult to use for companies with unpredictable or fluctuating cash flows, such as early-stage startups.
Net Asset-Based Valuation
Description: Calculates the market value of a company’s assets minus its liabilities to determine the net asset value. It’s often used for companies with significant tangible assets or in scenarios involving liquidation.
Pros:
-
- Simple and reliable for companies with substantial tangible assets.
- Provides a clear picture of the company’s net asset value.
- Useful for companies in industries like real estate or manufacturing.
Cons:
-
- Ignores the company’s future earnings potential.
- Not suitable for companies with significant intangible assets, like technology firms.
- Less relevant for going concerns that generate value through operations rather than assets.
Liquidation Valuation
Similar to the Net Asset Valuation Method but assumes assets are sold under distressed conditions, often at a lower value. Used when a company is facing bankruptcy or restructuring.
Pros:
-
- Provides a worst-case scenario for investors or creditors.
- Useful for risk assessment and during financial distress situations.
- Helps determine the minimum value of a company’s assets.
Cons:
-
- Typically yields lower values than other methods, reflecting a distressed sale.
- Not relevant for healthy, ongoing businesses.
- Does not account for any value generated from continued operations.
Precedent Transactions
Values a company based on multiples from past transactions involving similar companies in the same industry.
Pros:
-
- Provides a realistic view of market conditions and pricing trends.
- Useful in M&A scenarios where understanding deal dynamics is critical.
- Captures industry-specific premiums, such as those for strategic synergies.
Cons:
-
- Data may be difficult to obtain or inconsistent.
- Each transaction has unique circumstances, making it hard to generalize.
- Historical deals may not reflect current market conditions or future trends.
Why Is It Important
Valuation is at the heart of finance, as it determines how much a business or asset is worth.
Whether you’re looking to buy, sell, invest, or simply understand the financial health of your company, knowing how to value a company or asset is essential.
Mastering valuation helps make informed decisions and identify opportunities others might overlook.
Use Cases
Different situations call for different valuation approaches.
The Income Approach, using methods like Discounted Cash Flow (DCF), is best for valuing companies with predictable future cash flows to determine intrinsic value.
The market approach, with methods like comparative analysis and precedent transactions, is useful when ample market data is available to reflect current market sentiment and trends.
The Cost Approach, employing the Net Asset Method and Liquidation Valuation, is ideal for assessing asset-heavy or distressed companies, focusing on tangible asset value minus liabilities.
Pro Tip
Don’t rely on a single valuation method. Different scenarios require different approaches, and combining multiple techniques (when possible) gives a more rounded view of a company’s worth.
#3: Budget Process
Steps in the Budget Process
In this video, I explain to you the details of the key steps for creating a successful budget.
Set Expectations with Management
Begin by aligning financial goals with management expectations to ensure everyone is on the same page regarding revenue, expenses, and growth targets.
Sales Forecasting
Develop a sales forecast that forms the basis of the entire budget. This involves assessing market conditions and predicting future sales.
Operational Plan
Create an operational plan that includes production schedules, inventory management, and resource allocation.
Resource Allocation
Identify and allocate the resources needed to support the operational plan, including staffing, raw materials, and technology.
Standard Costs and Overhead
Calculate standard costs and overhead to understand the fixed and variable expenses involved in production.
Income Statement, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement
Develop these financial statements to provide a complete picture of the company’s financial health, aligning projected revenues and costs.
Why Is It Important
A well-planned budget is a roadmap for business success. It sets financial expectations, guides spending, and aligns resources with strategic goals.
A solid budget process helps mitigate risks, manage cash flow, and ensure that all departments work toward the company’s financial targets.
Use Cases
The budget process begins with setting expectations with management and proceeds through forecasting sales, creating operational plans, and determining resources.
Once standard costs and overhead are calculated, companies create income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
This comprehensive approach ensures that every aspect of the business is aligned and adequately funded.
Pro Tip
Always involve department heads in the budgeting process.
Additionally, utilize financial models and AI tools to automate data analysis, improve forecasting accuracy, and provide deeper insights for more strategic, data-driven decision-making.
#4: Reducing Costs
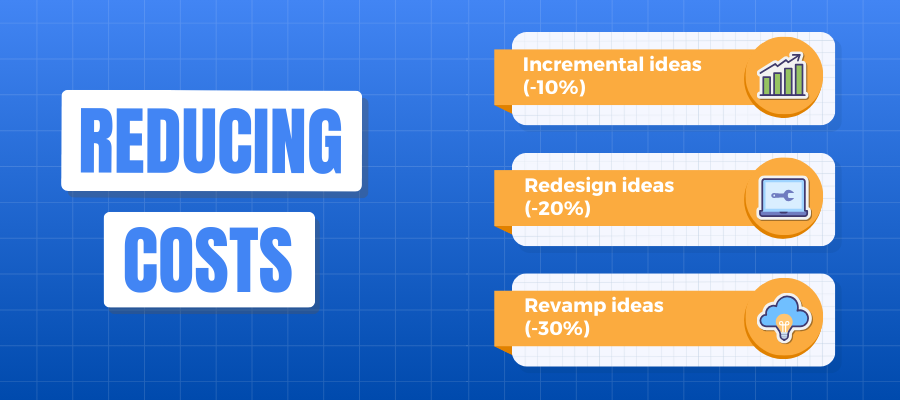
How to Do It
Reducing costs can be approached in three main ways:
Incremental ideas (-10%)
Start with smaller, gradual changes, such as gaining control over miscellaneous spending, reducing consulting services, or cutting department-specific expenses. These actions can lead to moderate savings while maintaining stability.
Redesign ideas (-20%)
Take a more significant step by redesigning workflows and eliminating inefficiencies. This might involve reducing business requirements, automating processes, or removing unnecessary liaisons and coordinators.
Revamp ideas (-30%)
For a deeper impact, consider restructuring cross-department activities, eliminating non-essential programs, or shifting tasks to more efficient locations. This is a comprehensive approach that can lead to substantial savings.
Why Is It Important
Reducing costs is crucial for any business aiming to remain competitive and increase profitability.
A company’s ability to manage and control costs can be the key difference between thriving in the market and falling behind.
Effective cost reduction not only improves the bottom line but also ensures the business has enough resources to invest in growth areas, innovation, and resilience during tough times.
Use Cases
Companies can implement cost-reduction strategies in different ways. Incremental ideas, such as reducing miscellaneous spending or scaling back consulting services, help control costs on a smaller scale.
Redesign ideas, like automating processes or reducing business requirements, allow for more significant savings.
Finally, revamping ideas, such as eliminating unnecessary programs or restructuring cross-department activities, provides deeper, structural reductions to expenses.
Pro Tip
Take a systematic approach to reducing costs. Start with incremental changes and gradually move to redesign and revamp efforts.
This way, your team can manage change more effectively and avoid unnecessary disruptions.
Final Thoughts
These four finance concepts – reducing costs, valuation techniques, the budget process, and PVM analysis – aren’t just theoretical concepts; they’re practical tools you can use to make a real impact.
By learning how to manage costs, accurately value a business, create a solid budget, and analyze price, volume, and mix, you’re positioning yourself as a crucial part of your company’s success.
These concepts are interconnected, and understanding them will help you make smarter decisions, optimize resources, and ultimately contribute to the growth and profitability of your organization.
Take the time to master them, and you’ll become an invaluable asset to your team.
FAQ
Q: How can I effectively reduce costs using incremental, redesign, and revamp ideas?
A: Reducing costs can be approached in stages. Start with incremental reductions to cut minor expenses, then move to redesign initiatives to streamline processes, and finally, use revamp strategies for bigger changes. This method ensures smoother implementation and effective cost management.
Q: When should I apply different valuation techniques?
A: Use Comparable Analysis when you have reliable data from similar companies, Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) for assessing intrinsic value when future cash flows are predictable, Net Asset Valuation Method for asset-heavy companies or when the going concern is in question, Liquidation Valuation in distressed scenarios, and Precedent Transactions for M&A, based on industry deal benchmarks. Applying multiple methods together is beneficial, as they complement each other and provide a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of value.
Q: What are the key steps involved in the budget process?
A: The budget process involves setting expectations with management, forecasting sales, creating an operational plan, allocating resources, calculating standard costs and overhead, and developing financial statements like income, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Reviewing the budget monthly ensures financial alignment.
Q: What do price, volume, and mix mean in PVM analysis?
A: Price refers to the impact of price changes on sales revenue, volume represents the effect of selling more units, and mix shows how selling a different combination of products affects revenue. Understanding these components provides clarity on revenue drivers and helps guide better strategic decisions.
Q: How can I use PVM analysis to improve profitability?
A: Regularly use PVM analysis to understand how price, volume, and product mix affect sales revenue. This can help identify areas where adjustments can increase profitability, such as improving pricing strategies or focusing on higher-margin products. You can apply discounted cash flow (DCF) to personal investments by estimating future cash flows from an asset (like rental income) and discounting them to present value. This helps in assessing whether an investment is worthwhile.