When it comes to analyzing a company’s financial health, two essential documents play a crucial role: the balance sheet and the income statement.
While they both provide valuable insights into a company’s financial performance, they serve distinct purposes.
Let’s dive in to understand their differences and importance!
Table of Contents
What Are The Differences between Balance Sheet and Income Statement?
Here is a detailed analysis of their differences.
Balance Sheet – A Snapshot in Time
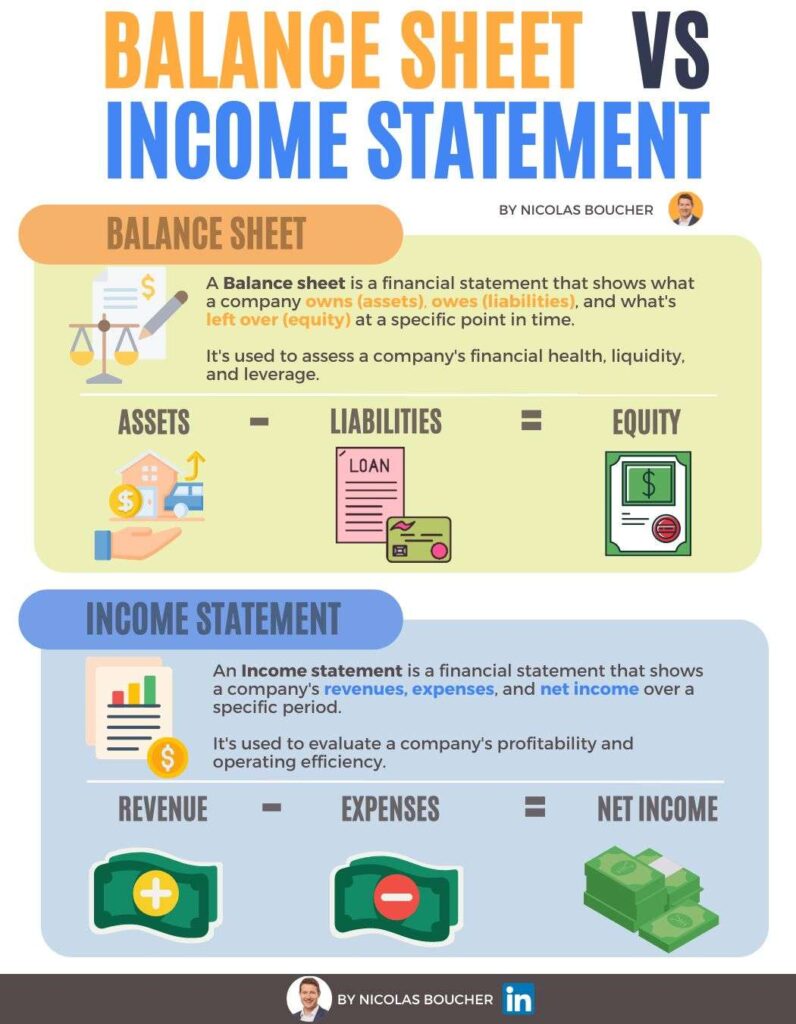
A balance sheet is akin to a photograph capturing a company’s financial position at a specific moment.
It provides a comprehensive overview of what a company owns (assets) and what it owes (liabilities) at that particular point in time.
The balance sheet consists of three key components: assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
Assets encompass everything a company owns, including cash, investments, property, equipment, and accounts receivable.
Liabilities represent the company’s financial obligations, such as loans, accounts payable, and accrued expenses.
Shareholders’ equity reflects the residual interest in the assets after deducting liabilities and represents the owners’ stake in the company.
Income Statement – A Video of Financial Performance
In contrast, the income statement presents a dynamic view of a company’s financial performance over a specific period, typically a month, quarter, or year.
It captures the revenues generated and expenses incurred during that timeframe.
The income statement begins with the company’s revenues, which may come from the sale of goods or services.
It then deducts various expenses, including the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, interest, and taxes, to arrive at the net income or profit.
While the balance sheet focuses on the company’s financial position, the income statement sheds light on its financial performance.
By examining the income statement, investors and analysts can evaluate a company’s ability to generate profits, identify trends in revenue and expenses, and assess its overall profitability.
Example of Using Balance Sheet and Income Statement
To illustrate the relationship between the balance sheet and the income statement, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario.
Company XYZ’s balance sheet reveals that it has $1 million in cash, $3 million in property and equipment, $500,000 in accounts payable, and $2 million in long-term debt.
The income statement shows that the company generated $5 million in revenue and had $4 million in expenses, resulting in a net income of $1 million.
In this example, the balance sheet provides a snapshot of Company XYZ’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity, while the income statement shows the company’s revenue, expenses, and net income over a specific period.
By analyzing both documents, investors can gain insights into the company’s liquidity, solvency, profitability, and overall financial health.
Bonus Tips
- Understand the Financial Statements: Familiarize yourself with the different financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, statement of cash flows, and statement of changes in equity. Each statement serves a distinct purpose and provides unique information about a company’s financials.
- Analyze the Structure: Pay attention to the structure of the financial statements. For example, in a balance sheet, assets are typically listed on one side, while liabilities and equity are listed on the other. Understanding the layout will help you navigate the information effectively.
- Look for Trends: Compare financial statements across different periods or benchmark them against industry standards to identify trends. This analysis can reveal areas of strength and weakness, helping you make informed decisions.
- Calculate Key Ratios: Utilize key financial ratios, such as liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, and debt ratios, to gain deeper insights into a company’s financial performance. These ratios provide valuable information about the company’s efficiency, profitability, and leverage.
- Combine Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis: While financial statements provide crucial quantitative information, it is equally important to gather qualitative insights. Engage with management, explore competitor strategies, and consider market dynamics to challenge and validate the figures presented in the financial statements.
Final Words – Both Are Crucial for Your Accounting Performance
Both the balance sheet and the income statement are indispensable tools for assessing a company’s financial health.
While the balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position, the income statement reveals its financial performance over a specific period.
By understanding the differences between these two statements and analyzing them in conjunction, investors and analysts can make informed decisions.
And also, identify trends, and gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial status.
If you are an accounting manager, ChatGPT can help you make your team more productive.
If you want to train your team on how to use ChatGPT in a business context, I can help you.
I have launched the first and only ChatGPT training for business. I have still some slots for the next 4 weeks but they are going fast. Check this page if you want to bring your team into a position to leverage AI for their work.
Key Takeaways
- The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder’s equity at a specific moment.
- The income statement captures a company’s financial performance over a specific period, showcasing revenues, expenses, and net income.
- Analyzing both the balance sheet and the income statement is crucial for a comprehensive assessment of a company’s financial health.
- Look for trends in the financial statements and calculate key ratios to gain deeper insights.
- Combine quantitative analysis with qualitative information to challenge and validate the figures presented in the financial statements.
FAQ
1. What’s a balance sheet’s main purpose?
- The balance sheet gives a snapshot of what a company owns and owes at a specific moment.
2. How does an income statement differ?
- The income statement shows how much a company earned and spent over a certain time.
3. What does a balance sheet include?
- The balance sheet has three parts: what the company owns (assets), owes (liabilities), and what’s left (owners’ equity).
4. What’s the point of the income statement?
- The income statement tells us if a company is making money or not and breaks down the earnings and expenses.
5. How do these statements help understand a company’s health?
- The balance sheet shows a financial snapshot, income statement tells the financial story. Studying both help know if a company’s doing well or not.