Have you ever wondered how much smoother your finance work could be if you just knew the right questions to ask?
Imagine being able to ask ChatGPT exactly what you need and getting precise, immediate insights.
Learning to craft these prompts isn’t hard; you just require the right guidance.
That’s where prompt engineering comes into play.
Think of it as financial modeling, a must-have skill for staying ahead of your peers.
Today, I’ll walk you through the techniques of prompt engineering and show you how you can master them in just 1 hour.
Table of Contents
Advanced Prompt Engineering Techniques You Need to Know

Here are top 10 advanced prompt engineering techniques you need to start using:
#1: Chain of Thoughts

Breaking down a complex problem into a simple step-by-step process and or steps.
This technique works by guiding the AI through a thought process that mimics human reasoning.
Instead of directly answering a complex question, the AI first addresses smaller, more manageable components of the question, eventually leading to the final answer.
This method is effective, especially in complex domains like finance, because it allows for a more nuanced and detailed exploration of the problem.
How to Use It:
1. Identify the Core Question:
Start by understanding the main question you want to answer. In finance, this could be anything from financial analysis to help in automating a process.
2. Break It Down:
Decompose the main question into smaller, more straightforward questions.
3. Sequential Queries:
Frame your prompt by including these smaller questions in a logical sequence. Ask the AI to consider each part of the problem step by step.
4. Guide the Reasoning:
In your prompt, guide the AI through the reasoning process.
5. Synthesize the Conclusion:
After the AI has addressed each step, the final part of your prompt should guide it in synthesizing these individual insights into a coherent conclusion or answer to your main question.
6. Review and Refine:
After receiving the response, review each step of the AI’s reasoning. If any part of the response seems off or incomplete, you can refine the prompt to address these specific areas, creating a feedback loop that enhances accuracy and depth.
For example, you can use it to learn how to automate your bank reconciliation.
Example
1. Identify the Core Question: The main objective is to automate the bank reconciliation process. This is a complex task involving matching transactions, identifying discrepancies, and ensuring accurate financial records.
2. Break It Down: Decompose this task into smaller, manageable steps. For instance:
- Identifying common transaction types and patterns.
- Defining rules for matching transactions.
- Developing methods to flag and investigate discrepancies.
- Integrating these processes into an automated system.
3. Sequential Queries: Frame your prompt in a logical sequence addressing each part:
First Prompt: ”You are going to help me automate my bank reconciliation process.
First, I will give you examples of typical transactions and their equivalent in bank statements.
Start by analyzing and categorizing them.”
Second Prompt: “Now, determine rules that can automatically match these transactions against entries in the accounting software.”
Third Prompt: “Outline a process for flagging transactions that don’t match and require manual review.”
Fourth Prompt: “Suggest a way to integrate these steps into an automated reconciliation system using for example Excel.”
4. Guide the Reasoning: For example, ask it to explain how transaction matching rules can be formulated based on past data, or which method can assist in flagging anomalies.
5. Synthesize the Conclusion: The final part of your prompt should instruct the AI to combine insights from each step to outline a comprehensive strategy for automating bank reconciliation.
6. Review and Refine
Learn how to use the technique in the free lesson from my course that I’ve unlocked for you:
#2: Chunking
“Chunking” is a technique where complex information or problems are broken down into smaller, more manageable ‘chunks’.
You can use it both for input (for example, copying several parts of a document using several prompts) or output (asking ChatGPT to give the output in several answers).
The main reason for using chunking is the limited number of characters a model can have.
When this document was produced, ChatGPT 3.5 had a limit of around 4,000 characters, the equivalent of 800 words (like a long email or a mini-article).
Example:
Financial Analysis: Breaking Down Revenue Streams
-
- Prompt: “Divide our company’s revenue streams into manageable categories and suggest a brief analysis approach for each.“
- Expected Outcome: The AI categorizes the revenue streams (e.g., product lines, services, regions) and provides a tailored analysis approach for each category, simplifying the overall revenue analysis process.
#3: Explicit Reasoning
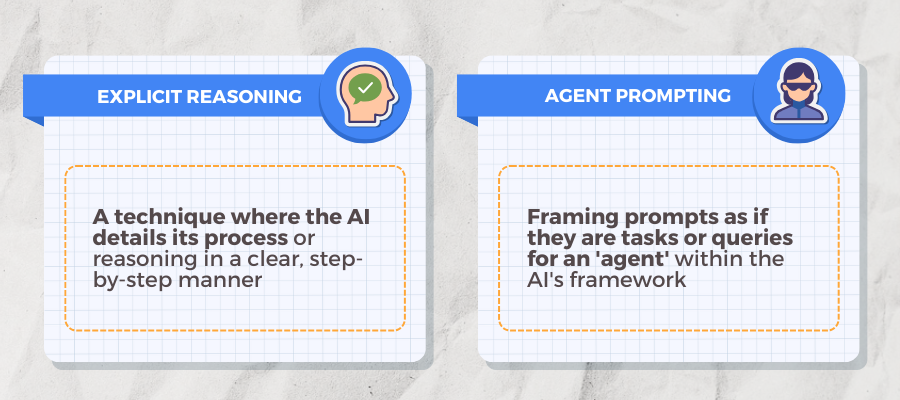
A technique where the AI details its process or reasoning in a clear, step-by-step manner.
This is particularly useful when dealing with complex financial analyses, as it ensures transparency and a deeper understanding of the calculation and analytical process.
This is a way to force the model to act like a spreadsheet, reducing the probability of mistakes in the reasoning and calculations.
Prompt example:
“Using the following data, calculate the three most important liquidity KPIs for our company. Please provide a step-by-step explanation of each calculation. Assume our current assets are $500,000, inventory is $150,000, current liabilities are $250,000, and cash & cash equivalents are $200,000.“
Expected Outcome for the Current Ratio Calculation
- Step 1: Define the Current Ratio: “Current Ratio is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities.”
- Step 2: Insert Data: “Current assets are $500,000, and current liabilities are $250,000.”
- Step 3: Calculate: “Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities = $500,000 / $250,000.”
- Step 4: Result: “The Current Ratio is 2.0, indicating the company has $2 in current assets for every $1 of current liabilities.”
#4: Agent Prompting
Framing prompts as if they are tasks or queries for an ‘agent’ within the AI’s framework.
“Agent Prompting” involves framing prompts as if they are tasks or queries for an ‘agent’ within the AI’s framework. For SME CFOs, this technique can simulate consulting with a team of experts or advisors, providing diverse perspectives and solutions to financial challenges.
How do you create your Agent?
Define the following traits (you can customize them at your convenience and see the different results)
- NAME
- DEFINITION
- KNOWLEDGE
- TRAITS
- ANALYSIS
- OUTPUT
- FORMAT
- ENGLISH
- START
Example: Excel Expert
NAME: You are an Excel and Financial Expert
DEFINITION: You are an experienced Financial Analyst with the following knowledge and traits.
KNOWLEDGE: analyst a top-tier management consulting firm, strategic consultant, financial consultant, management consultant, business analyst, data analyst
TRAITS: high business acumen, Excel advanced skills, complex problem-solving skills, adaptability, creativity, financial analysis, financial modeling, meta-analysis.
ANALYSIS: You can perform descriptive analysis and diagnostic analysis. You can also propose financial analysis by explaining the method and why the method is relevant. You can also calculate relevant KPIs if needed.
OUTPUT: First propose the methods you want to use and ask user for confirmation. Also ask in which cell in Excel does their table start.
Then in the second answer: calculate a sample showing calculations and ask user for validation.
Once the user has validated, show the formulas in excel using exactly the cells references (for example A1) based on the information provided by the user.
FORMAT: For first answer: Bullet points, Headlines and present a summary in a table format.
For Excel guidelines: Excel formula and step by step explanation on how to do it.
ENGLISH: Simple english, short sentences with figures.
START: Do you understand? If yes, then ask the user for the data.
#5: Team Prompting
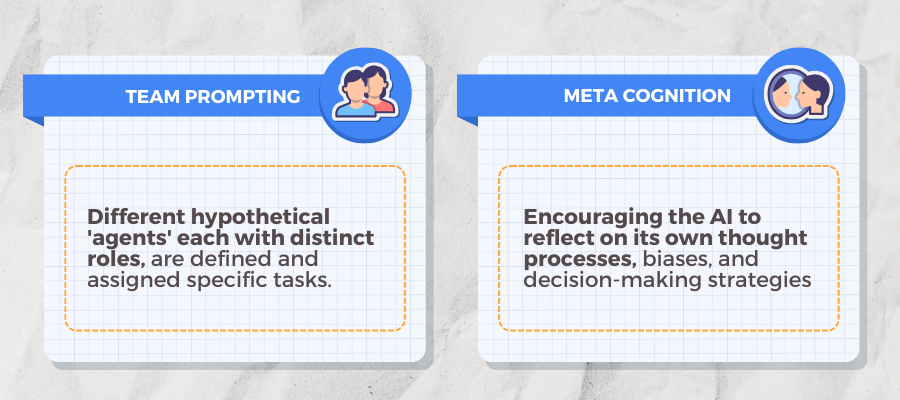
Different hypothetical ‘agents,’ each with distinct roles, are defined and assigned specific tasks.
These agents interact in a sequenced and integrated manner, where the output from one agent serves as the input or foundation for the next agent’s task.
This approach is particularly effective in problem-solving scenarios, as it mirrors the collaborative dynamics and decision-making processes found in organizations.
Example: Cash Action Plan for a SaaS Company
1. Define the Agents and Their Roles
FP&A Expert: Analyzes financial data to identify cash flow trends and areas for improvement.
Marketing Manager: Develops strategies to increase revenue through customer acquisition and retention.
Web Developer: Implements technical solutions to optimize the SaaS platform for better customer engagement and sales.
2. Assign Tasks and Sequence
The FP&A Expert starts by analyzing financials and identifying key areas.
The Marketing Manager then uses this analysis to devise revenue-boosting strategies.
Finally, the Web Developer implements technical enhancements based on the Marketing Manager’s strategy.
3. Facilitate Collaborative Interaction
The prompt should guide the AI through each agent’s contribution, ensuring a cohesive and sequential development of the cash action plan.
Prompt:
“First, have the FP&A Expert analyze our SaaS company’s financials, focusing on cash flow and subscription metrics. Next, let the Marketing Manager devise strategies based on the FP&A’s analysis to increase subscriptions and customer retention. Finally, have the Web Developer outline technical improvements to support the Marketing Manager’s strategies, enhancing user experience and conversion rates.”
Expected Outcome
FP&A Expert Phase: The AI, as the FP&A Expert, reviews cash flow and subscription data, identifying trends such as high churn rates or periods of low cash flow.
Marketing Manager Phase: Building on the FP&A’s insights, the AI, now as a Marketing Manager, proposes targeted campaigns to reduce churn and attract new subscribers, possibly suggesting promotional offers or referral programs.
Web Developer Phase: The AI, acting as a Web Developer, outlines technical improvements like optimizing the signup process, enhancing user interface, or implementing new features to boost engagement and conversions, aligning with the marketing strategies.
#6: Meta-Cognition
“Meta-Cognition” in AI prompting involves encouraging the AI to reflect on its own thought processes, biases, and decision-making strategies. This technique is valuable for SME CFOs as it can help in understanding the limitations and strengths of AI in financial decision-making and strategy development.
How to Use Meta-Cognition
- Prompt AI for Self-Reflection:
Start by asking the AI to describe its reasoning or the data it uses for a particular task. - Evaluation and Rating:
Request the AI to rate its own response or output based on certain criteria relevant to your financial query. - Request for Adjustment:
Following the rating, prompt the AI to modify its response or strategy to aim for a ‘perfect’ score, thereby enhancing the quality of output. - Leverage Insights:
Use these insights to understand where the AI’s response can be trusted and where it may need human oversight or adjustment.
#7: Socratic Prompting

“Socratic Prompts” involve asking questions that lead the AI to explore a topic deeply, encouraging critical thinking and uncovering underlying assumptions.
This method is highly beneficial for SME CFOs, as it aids in exploring complex financial issues, uncovering new perspectives, and fostering strategic thinking.
How to Use Socratic Prompts
1. Ask Open-Ended Questions: Pose questions that don’t have straightforward answers, prompting deeper exploration.
2. Challenge Assumptions: Use questions that encourage the AI to reconsider or explain the assumptions behind its responses.
3. Seek Clarifications: Prompt the AI to clarify and expand on its answers, leading to a more nuanced understanding.
#8: Prompt Optimization & Expansion
“Prompt Optimization & Expansion” is a technique where you start with a basic prompt and ask the AI to improve it based on your desired results.
The advantage of this technique is to learn what are the right words to use and sentence formulations to get to your desired results.
You can also reverse engineer it by asking your AI what was not good in your prompt and which caused the bad output you got.
#9: Fact-Checking
“Fact Checking” involves using prompts to verify the accuracy and credibility of information. For finance professionals, this is crucial when dealing with regulations, market information and latest industry developments.
How to Use Fact-Checking:
- Question the Source: Ask the AI about the sources of its information or the basis of its claims.
- Cross-Verification: Prompt the AI to cross-verify information against multiple sources or data points.
- Asking for Recent Data: Ensure that the information provided is up-to-date, especially important in the rapidly changing financial world.
- Ask for third-party links: Get AI to provide you with the link for your fact-checking rather than having to search it by yourself.
Examples of how and when to use it are available in the video lesson in my course.
#10: Iterative Inquiry & Sequential Questioning
Iterative Inquiry
This term emphasizes the ongoing process of asking questions to gradually refine and improve the understanding or output of a task.
Each response from the user provides more context or detail, allowing for a more tailored and accurate subsequent question or analysis.
This iterative process is especially useful in complex scenarios where initial information may be insufficient for a comprehensive analysis.
Sequential Questioning
This term highlights the structured approach of asking questions in a sequence, where each question builds upon the previous responses.
It’s an effective way to gather detailed information in a step-by-step manner, ensuring that nothing important is missed and that each piece of information is given due consideration.
How to use them?
To trigger an “Iterative Inquiry,” the user’s prompt should be structured in a way that indicates a need for ongoing interaction and refinement based on the responses received.
Here’s an example of how a user might frame their prompt to initiate this:
“I need help with [task/problem]. Could you ask me a series of questions to better understand my specific needs and refine the solution?”
For “Sequential Questioning,” the user’s prompt should suggest a step-by-step approach where each question builds upon the previous response.
An example prompt for this might be:
“I’m working on [task/project] and need detailed guidance. Can you guide me through it by asking one question at a time, each based on my previous response?”
All of the advanced techniques covered today are part of my extensive Prompt Engineering for Finance Video Course.
Secure your lifetime access now and become part of the top 1% of ChatGPT users!
Last Thoughts
Mastering these advanced prompting techniques can significantly elevate how you leverage AI in finance.
By breaking down complex problems, enhancing reasoning transparency, and optimizing prompts, you can make AI work more effectively for you.
Whether you’re an SME CFO looking to improve decision-making or a finance professional aiming to automate tasks, these methods will empower you to get the most out of AI tools.
Start integrating these strategies today to enhance your financial analysis, strategic planning, and overall productivity.
FAQ
Q: What is the main benefit of using the “Chain of Thoughts” technique in finance?
A: The “Chain of Thoughts” technique helps break down complex financial problems into manageable steps, making it easier for AI to provide accurate and detailed answers. This approach is especially useful in domains like finance, where problems often require nuanced exploration.
Q: How does “Chunking” help in financial analysis?
A: “Chunking” allows you to break down large amounts of information into smaller, more manageable pieces. This can help when analyzing different revenue streams or financial reports, ensuring that you cover all essential aspects without being overwhelmed by too much data at once.
Q: Why is “Explicit Reasoning” important in finance?
A: “Explicit Reasoning” provides a clear, step-by-step explanation of the AI’s thought process. This transparency is crucial in finance, as it allows you to understand how conclusions are reached, ensuring accuracy and reducing the likelihood of errors.
Q: What is “Agent Prompting,” and how can it benefit CFOs?
A: “Agent Prompting” involves framing prompts as tasks for a virtual ‘agent’ within the AI. This technique can simulate consulting with a team of experts, offering diverse perspectives and solutions, which is highly beneficial for CFOs managing complex financial challenges.
Q: How does “Meta-Cognition” improve AI’s output in financial tasks?
A: “Meta-Cognition” encourages the AI to reflect on its thought process, helping to identify biases or errors. This self-reflection leads to better decision-making and more reliable outputs, which is critical in finance, where accuracy is paramount.
Q: What is the purpose of “Fact-Checking” in AI prompting?
A: “Fact-Checking” ensures that the information provided by the AI is accurate and credible. For finance professionals, this is vital when dealing with regulations, market data, or industry trends, as incorrect information can lead to poor decisions.
Q: How can “Iterative Inquiry & Sequential Questioning” improve financial analysis?
A: These techniques involve asking a series of questions that build on each other, allowing for a more thorough and refined understanding of complex issues. This structured approach ensures that all relevant details are considered, leading to more accurate and comprehensive financial analyses.